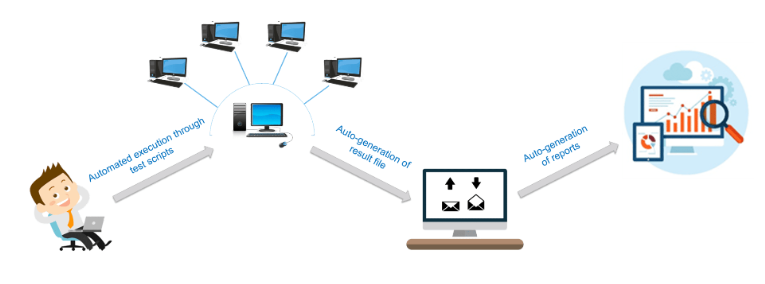
Selenium Automation
Apr 12th, 2023
BEST PRACTICES FOR SELENIUM AUTOMATION
In this blog post, we ll learn about best practices when developing scripts with selenium for web applications.
Introduction: Selenium is an open-source framework that is widely used for automating web browsers. It allows developers and testers to write scripts in various programming languages like Python, Java, and C# to automate interactions with web browsers.
Selenium provides a suite of tools for automating web browsers, including the Selenium IDE, Selenium WebDriver, and Selenium Grid. The Selenium IDE is a browser extension that provides a record-and-playback feature for creating test scripts. The Selenium WebDriver is a library that allows developers to control the browser programmatically using code. Finally, Selenium Grid is a tool for running tests on multiple browsers and platforms in parallel.
Selenium is used for web application testing, as well as for web scraping and data extraction. It supports a variety of browsers, including Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge, and can be used on multiple operating systems like Windows, macOS, and Linux. Selenium is a powerful tool for automating browser interactions and testing web applications, making it an essential tool for many developers and testers.
What Are The Advantages Of Selenium?
Selenium is a powerful tool for automated testing of web applications, and it offers several advantages:
Cross-browser testing: Selenium supports multiple web browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Internet Explorer, enabling developers to test their web applications across different browsers.
Language support: Selenium supports several programming languages such as Java, Python, Ruby, C#, and JavaScript, allowing developers to choose the language they prefer.
Open-source: Selenium is open-source software, meaning it is free to use and there is a large community of developers contributing to its development.
Easy integration: Selenium can easily integrate with other tools and frameworks like TestNG, JUnit, and Maven, making it easy to incorporate into your development process.
Record and playback: Selenium allows you to record your test scripts and play them back, making it easy to automate repetitive tasks and save time.
Flexibility: Selenium provides a lot of flexibility and customisation options for developers. You can customise your test scripts and create custom functions to suit your specific needs.
Simulates user actions: Selenium can simulate user actions like clicking, scrolling, and typing, allowing developers to test their web applications as if they were being used by real users.
BEST PRACTICES:
1. USING THE RIGHT LOCATORS
For testing the desired web elements of a particular application, QAs need to be proficient in using different locator strategies. After all, if the test scripts cannot identify the correct elements, the tests will fail.
Example: For automating inputs to the Username and Password fields of a login page, the primary step is to locate those text fields. If the script cannot find the Username and Password fields, the login process will not work.
2. IMPLEMENTING PAGE OBJECT MODEL
With ever-increasing customer demands, a website’s UI is bound to evolve after incorporating new changes at regular intervals. Needless to say, locators corresponding to specific UI elements change too. This means QAs need to create new test cases for the same page again, which can be tedious.
One can address this by using the POM (Page Object Model) design pattern for creating test scripts. In this design pattern, each web page is considered a class file, and every class file carries corresponding web elements. This technique helps eliminate code duplication and also makes test maintenance more convenient. QAs can also reuse the existing code and make minimal changes.
3. RUNNING SELENIUM TESTS ON REAL DEVICES
Although there are multiple emulators available on the internet for Selenium testing across platforms, running tests on real devices makes a considerable difference.
Emulators are just software programs that mimic the functionality of a device. They are more suitable for testing code changes in the initial stages of development. Besides, emulators for each device-OS combination may not be available, which makes it even more challenging for QAs to test on desired combinations.
Accurate results can only be expected when websites are tested in real user conditions. This allows teams to discover maximum bugs and eventually roll out a robust application. Teams can leverage cloud-based platforms like BrowserStack that offer a cloud selenium grid of 3000+ real browsers and devices. This makes it convenient for QA engineers to perform comprehensive cross-browser and device testing across platforms. One can also integrate their test pipelines with CI/CD tools.
4. TAKE SCREENSHOTS WHEN A TEST FAILS
It is inevitable that Selenium scripts will fail at some point or another. A major issue in this regard is figuring out why the failure occurs – a bug in the AUT or an error in the code. To remedy this, set up the test infrastructure to take screenshots whenever a failure occurs. This will make it much easier to investigate and identify the cause of test failure, saving the testers’ time and effort.
5. USE THE BROWSER COMPATIBILITY MATRIX
To start with, it is a challenging task to narrow down a list of browsers (browser versions, too) and operating systems to run automated tests on. To manage this task, it is recommended that you use a browser compatibility matrix.
A browser compatibility matric draws vital data from multiple metrics – browser, device, and OS usage numbers, product analysis, target audience preference, and more. It then limits test coverage to a specific set of browsers and devices. Essentially, it restricts the scope to the most relevant browser-OS combinations, thus making the process more manageable.
6. INCORPORATING WAIT COMMANDS
Web browsers take some time to load individual web pages. The page load speed is subjective to network conditions, server issues, or system configurations. To deal with this, QAs often use the Thread.sleep() method, which pauses the automation script for a specified amount of time.
However, this is not the most efficient method. In some cases, a website may take longer to load than the specified time. On the other hand, a website may load quicker than the specified time, resulting in slower test execution. A better, more efficient alternative is to use Implicit or Explicit Waits.
7. PLANNING AND DESIGNING TEST CASES BEFOREHAND
QA teams must have a proper test plan in place before getting started with automation. QA engineers must think about all logical scenarios and create extensive test cases from the end-users’ perspective. Diving straight into automation without a concrete strategy usually leads to bottlenecks in the later stages.
Often, QAs focus more on verifying whether the scripts run successfully rather than planning for extensive test scenarios. This approach is ineffective for ensuring full-proof testing of web applications.
8. IDENTIFYING AND PRIORITIZING TEST CASES
Testing complex web applications can be challenging at times. Prioritizing certain test cases over others makes it easier to achieve test coverage goals. QAs must have clarity on which test cases are critical and need to be executed on priority.
Example: A login page is a vital part of any web-application. Naturally, automating tests to verify the login page makes sense. This is because the login page rarely undergoes any modifications but offers an important function. Thus, testing it would be easy, and running the tests would cover a high priority task in the pipeline early on.
In summary, Selenium automation seeks to reduce manual testing efforts, increase execution speed, and identify the maximum number of bugs at the earliest. However, in order to get the most out of their selenium scripts, QAs must follow the best practices highlighted above. This will also help in establishing a reliable test cycle.